Amino acid sequences and evolutionary relationships answers key – Unveiling the profound significance of amino acid sequences in unraveling the tapestry of evolutionary relationships, this guide delves into the intricacies of these molecular building blocks and their pivotal role in shaping the narrative of life’s diversification.
Through meticulous analysis of amino acid sequences, scientists have illuminated the intricate connections between organisms, shedding light on their shared ancestry and evolutionary trajectories. This comprehensive guide explores the diverse methodologies employed to decipher these sequences, revealing their profound implications for our understanding of the tree of life.
Amino Acid Sequences and Evolutionary Relationships
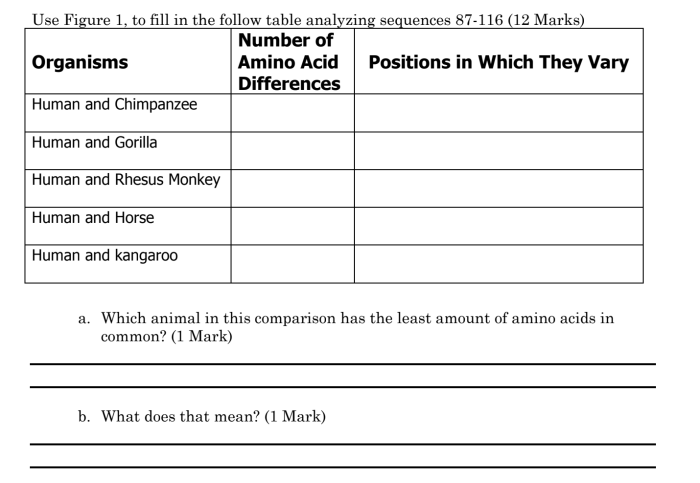
Amino acid sequences, the linear arrangement of amino acids in proteins, play a crucial role in determining the evolutionary history of organisms. These sequences contain information about the genetic relatedness between species and provide insights into the processes of evolution.
The significance of amino acid sequences lies in their conservation across species. Essential proteins, responsible for critical cellular functions, tend to have highly conserved sequences over long evolutionary periods. This conservation suggests that these sequences have been maintained throughout evolution due to their functional importance.
Methods for Analyzing Amino Acid Sequences, Amino acid sequences and evolutionary relationships answers key
To analyze amino acid sequences for evolutionary relationships, various methods are employed, each with its strengths and weaknesses:
- Pairwise Alignment:Compares two sequences to identify similarities and differences, providing a measure of sequence relatedness.
- Multiple Sequence Alignment:Aligns multiple sequences to identify conserved regions and patterns, allowing for more comprehensive comparisons.
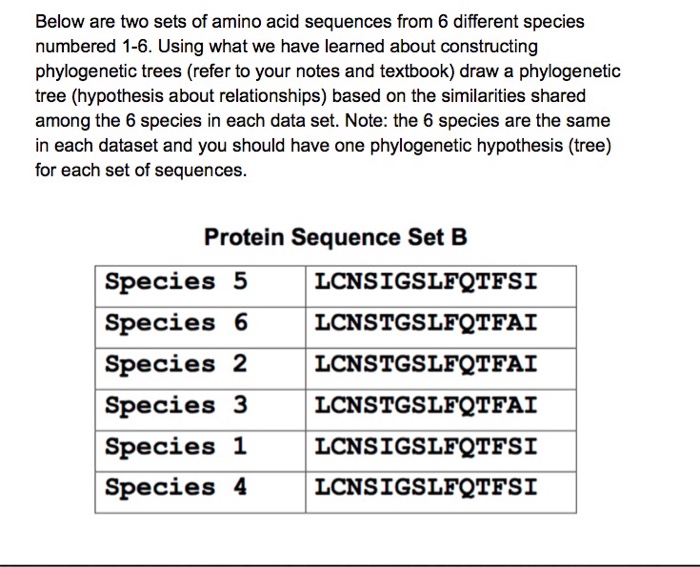
- Phylogenetic Analysis:Uses aligned sequences to construct phylogenetic trees, representing the evolutionary relationships among species based on shared ancestry.
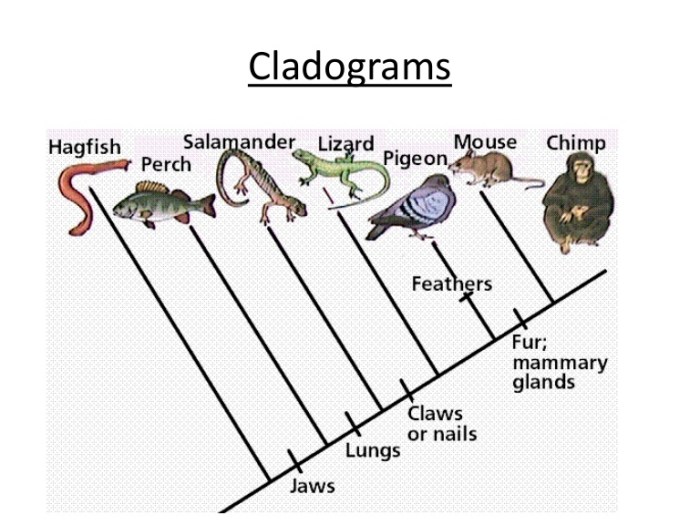
Phylogenetic Trees and Amino Acid Sequences
Phylogenetic trees are branching diagrams that depict the evolutionary history of species based on their shared characteristics. Amino acid sequences provide valuable data for constructing phylogenetic trees:
- Molecular Clock:Assumes a constant rate of sequence evolution, allowing for the estimation of divergence times between species.
- Parsimony:Favors trees that require the fewest evolutionary changes, providing a more conservative estimate of relationships.
Applications of Amino Acid Sequence Analysis
Amino acid sequence analysis has numerous practical applications in various fields:
- Medicine:Identifying disease-causing mutations, developing new drugs, and understanding the molecular basis of genetic disorders.
- Biotechnology:Engineering proteins with improved properties, creating new enzymes for industrial processes, and developing genetically modified crops.
- Forensics:DNA analysis for identification, paternity testing, and solving crimes.
Ethical implications of using amino acid sequence analysis include issues related to privacy, discrimination, and the potential misuse of genetic information.
FAQ Summary: Amino Acid Sequences And Evolutionary Relationships Answers Key
What is the significance of amino acid sequences in evolutionary studies?
Amino acid sequences provide a molecular record of evolutionary history, as they are highly conserved across species and can reveal shared ancestry.
How are amino acid sequences used to construct phylogenetic trees?
Phylogenetic trees are constructed by comparing amino acid sequences from different species and identifying patterns of similarity and difference. These patterns can be used to infer evolutionary relationships.
What are the ethical implications of using amino acid sequence analysis?
Amino acid sequence analysis has ethical implications related to privacy, discrimination, and the potential misuse of genetic information.