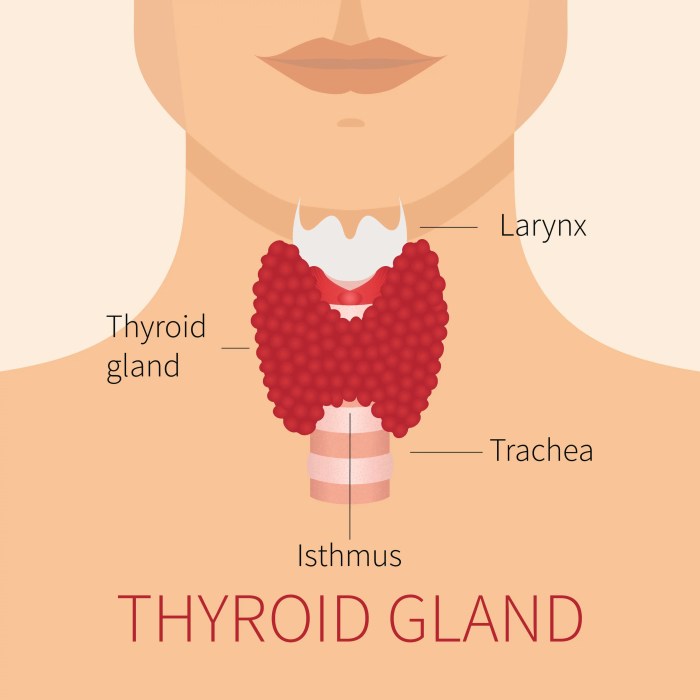
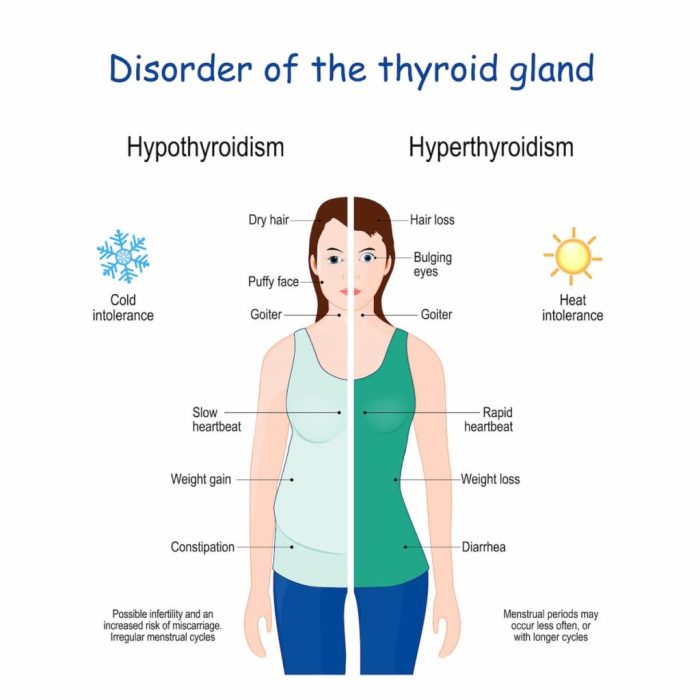
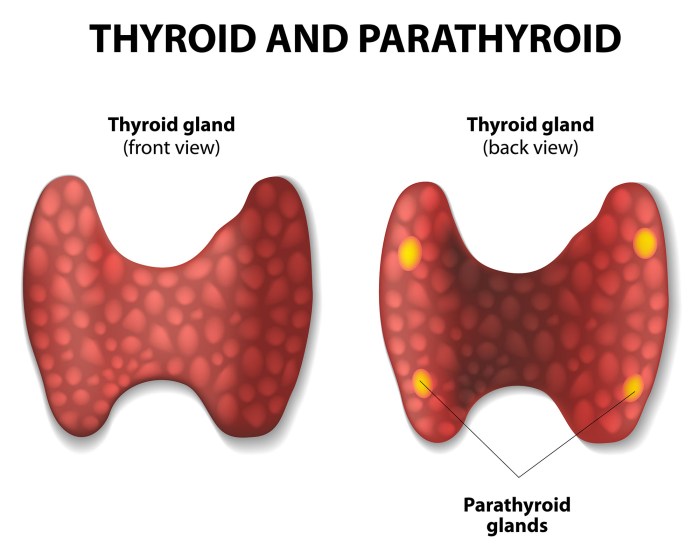
Which gland is not matched with its type of secretion – In the intricate tapestry of human physiology, glands play a pivotal role, orchestrating the secretion of vital substances that regulate countless bodily processes. However, in some instances, a mismatch arises between glands and their corresponding secretions, leading to a fascinating paradox in glandular function.
This article delves into the intriguing realm of gland-secretion mismatches, exploring the causes, consequences, and implications of this phenomenon. By unraveling the complexities of glandular physiology, we gain a deeper appreciation for the delicate balance that sustains our health.
Types of Glands
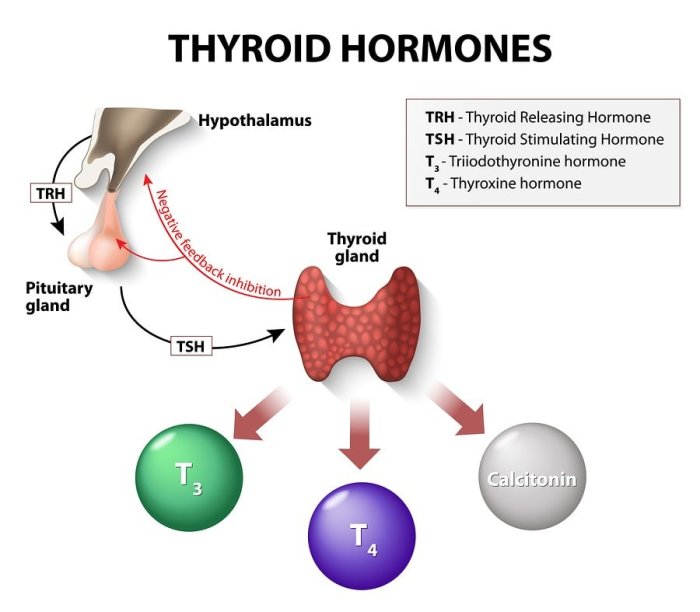
Glands are specialized cells or groups of cells that produce and secrete substances. Secretions are substances released by glands that perform various functions in the body.
Glands are classified based on their structure and the type of secretion they produce.
Types of Glands Based on Structure
- Exocrine glands: These glands have ducts that carry secretions to the surface of the body or to the lumen of an organ.
- Endocrine glands: These glands do not have ducts. Instead, they release their secretions directly into the bloodstream.
- Paracrine glands: These glands release their secretions into the interstitial fluid, which then affects nearby cells.
- Autocrine glands: These glands release their secretions, which then bind to receptors on the same cell that produced them.
Types of Glands Based on Secretion, Which gland is not matched with its type of secretion
- Serous glands: These glands secrete a thin, watery fluid that contains enzymes.
- Mucous glands: These glands secrete a thick, viscous fluid that contains mucin.
- Mixed glands: These glands secrete a combination of serous and mucous secretions.
- Hormonal glands: These glands secrete hormones, which are chemical messengers that regulate various body functions.
FAQ Summary: Which Gland Is Not Matched With Its Type Of Secretion
What are the potential causes of gland-secretion mismatches?
Mismatches can arise from genetic mutations, developmental abnormalities, or acquired conditions that disrupt the normal signaling pathways involved in glandular secretion.
How do gland-secretion mismatches affect the body?
Consequences can range from mild imbalances to severe disruptions in physiological processes, depending on the gland and secretion involved.
Are gland-secretion mismatches common?
While some mismatches are relatively common, others are rare and may indicate underlying medical conditions.